AliBERT

The first French-language Natural Language Processing (NLP) model specialized in the biomedical field
AliBERT is a pre-trained model for the recognition of clinical entities (pathologies, anatomies, diagnoses, etc.) in a medical report, i.e. Named Entity Recognition (NER).
Launched at the end of 2022, the AliBERT project has already produced its first scientific publication.
AliBERT is characterized by its ability to perform a wide variety of tasks, with virtually unlimited potential when fed with a set of annotated examples, usually in the range of a few hundred to a few thousand.

Named Entity Recognition*
- Dosage
- Clinical entities
- Oncology entities
- Personal data for document pseudonymization
Text classification**
- Detection of a causal relationship in a sentence
- Adverse event quantification
- Specialty Classification
Relation Extraction
- Drug ⇾ Dosage
- Diagnosis ⇾ Treatment
- Location ⇾ Laterality
*Detection of dosage (drug, dosage, frequency), detection of clinical entities (anatomy, pathologies, procedures), detection of oncological entities (histology, grade, stage, cancer location, etc.), detection of personal data for document pseudonymization (last name, first name, age, address, e-mail, phone).
**Detection of a causal relationship in a record, Adverse Event Qualification (mild, moderate, severe), Type of Specialty Classification (oncology reports, hospitalization reports, prescriptions, multidisciplinary reports).
AliBERT builds a specialized corpus of clinical and biomedical texts with a level of accuracy unmatched in the French-language medical field.
AliBERT has been pre-trained using a classical transformer architecture (BERT) on a corpus of 600,000 documents of different types. This corpus contains in particular articles from the biomedical literature, drug inserts, theses, and a few clinical reports.
AliBERT masters a maximum number of specialized words in the clinical and biomedical fields thanks to its optimized tokenizer, essential for the encoding of words in digital form, surpassing its contemporaries DrBERT and CamemBERT-bio in this field.
By pre-training the model on a biomedical corpus, AliBERT is able to build a “dictionary” of concepts and to position them in relation to each other, both in terms of semantic and contextual proximity. A word is considered both for its absolute meaning and for its position in a sentence.
For example, the word “tumor” may be associated with the word “cancer” when the context indicates malignancy, or simply with the word ” excrescence” when the context refers only to benign elements.
The example below gives an idea of AliBERT’s ability to guess the right word based on context:
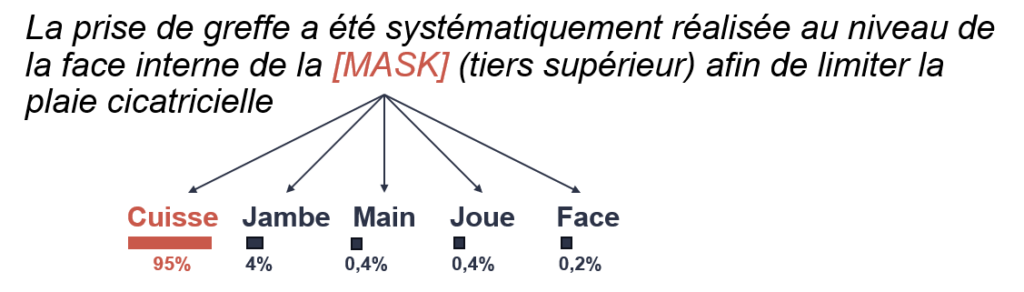
Example of word recognition in a biomedical text..
Biomedical NLP in French, a relatively unexplored field so far
The advent of so-called “transformers” models in 2017, and more recently in 2021, has revolutionized natural language processing (NLP) in a spectacular way. A wide range of NLP tasks can now be easily performed using these technologies, sometimes with very high levels of performance. However, these models still suffer from a number of limitations and are not always able to handle the French language use cases specific to the healthcare sector.
- LLMs (Large Language Model) are now multilingual, but recent studies show that they do not necessarily match the performance of transformers (e.g. BioBERT) in technical areas such as clinical or biomedical language.
- On the other hand, there areonly a few transformers specifically designed for the French language, and if they exist, they often deal with everyday language (CamemBERT, JuriBERT, BERTTweetFR).
To fill this gap, AliBERT was created, named after Jean-Louis Alibert, a 19th century physician considered the founder of dermatology in France.
The dual objective of this model is to handle high-performance use cases in the biomedical field and in the French language.
AliBERT performs very well in a wide range of use cases and is a state-of-the-art reference in the field of biomedical French language.

